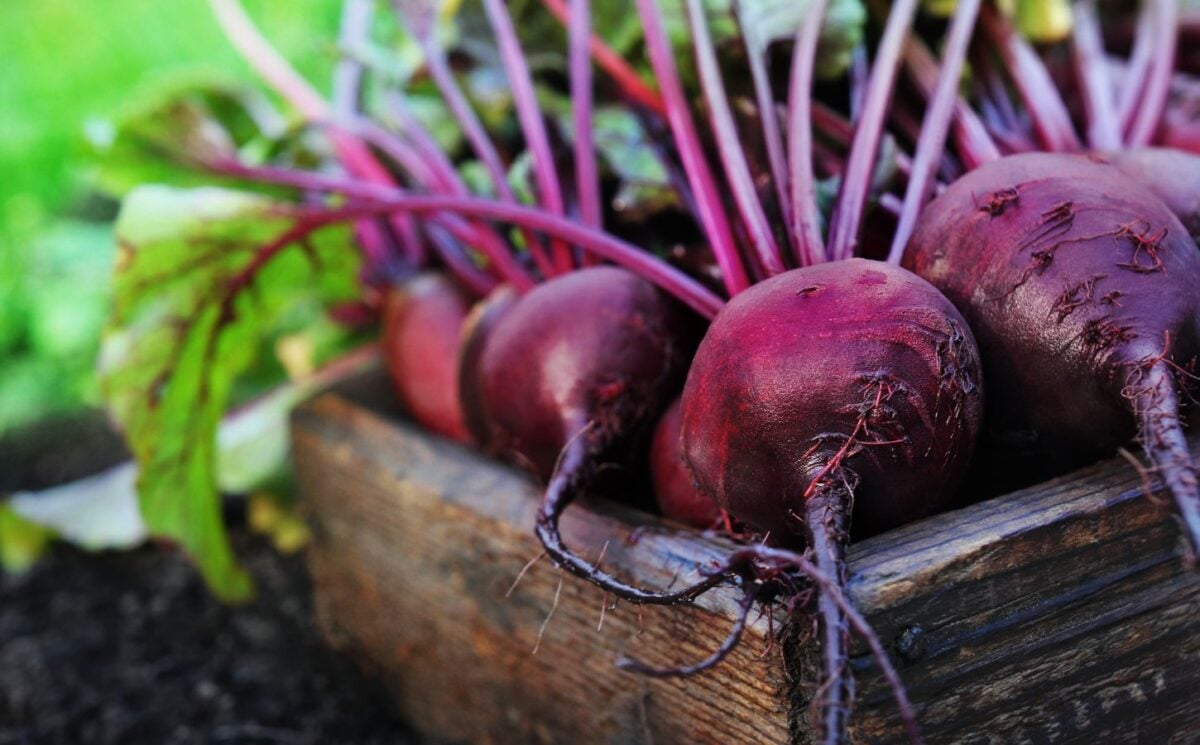
Beets have long been praised for their earthy flavor and bright color, but according to new research, their impact on the human body goes far deeper. Have you ever wondered what happens after you eat beets?
In a recent video, Plant Based Science London explores how eating just a couple of beets can spark a chain reaction inside the body, one that science says can improve blood flow, reduce inflammation, and even protect against disease.
Read more: Beetroot And Chickpea Coconut Curry
The video breaks down the science behind these effects, showing what happens in the first few hours after eating beets and why they’re considered one of nature’s most powerful functional foods.
Find out how compounds like betalains and nitrates influence blood pressure, energy production, and overall health, with a deeper look at how this simple root vegetable can make a measurable difference in just three hours.
The power of betalains
The video opens with the claim that beets contain a pigment compound called betalain. Betalain is found only in a handful of foods, including cactus pear, Swiss chard, and beetroot. This compounds, the narrator explains, possess “powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, cancer chemopreventive properties, and immunomodulatory activity.”
According to the research cited, betalains may help combat inflammation, slow oxidative stress, and even reduce the risk of certain cancers. Scientists have been so impressed by these results that they’re now investigating whether beet extracts could be used therapeutically to fight chronic inflammatory diseases such as liver disease and arthritis.
Nature’s nitric oxide booster
Beyond their color, beets stand out for another reason: their high nitrate content. Once ingested, these nitrates convert into nitric oxide, a compound that widens blood vessels and improves circulation. “Nitrates are converted into nitric oxide, a molecule that dilates blood vessels, causing blood pressure to drop,” the narrator explains.
One study cited in the video tracked “15 adults with stage 1 hypertension”. According to the video, participants drank either eight ounces of beet juice or water with low nitrate content. Over the next 24 hours, researchers found that those who consumed the beet juice experienced a drop in blood pressure by about 10 millimeters of mercury. The most significant change occurred between three to six hours after consumption.
That time window, around the three-hour mark, is when beets appear to reach their full cardiovascular potential. The effect, while temporary, is measurable and consistent, reinforcing the case for regular consumption.
Fuel for the body and brain
The video concludes by noting another lesser-known benefit of nitrates: improved cellular efficiency. Nitrates appear to enhance how mitochondria, the “powerhouses” of cells, generate energy. This effect improves stamina and endurance, which is why athletes often turn to beet juice before training.
From better blood flow to antioxidant protection, the studies show that this humble root vegetable earns its superfood reputation through measurable, science-backed benefits. Whether roasted, juiced, or blended into a smoothie, beets prove that small dietary changes can lead to big results in just a few hours.
Find more plant-based nutrition and health videos on Plant Based Science London’s YouTube channel.
Read more: How To Make This 10-Minute Creamy Beetroot Pasta