Oat milk has surged in popularity in recent years as more and more consumers move away from dairy. Free from major allergens like dairy, nuts, and soy, oat milk is regarded as a versatile and tasty all-rounder alternative milk. It performs well in everything from coffee and cereals to hot chocolates and baking. But how is the dairy-free drink made? And can you make oat milk yourself?
What is oat milk?
Milk from oats? You betcha! Oat milk is not only possible, but hugely popular – and it’s skyrocketed in popularity around the world over the last few years.
People associate oat milk with a naturally creamy texture and slightly sweet, mild taste. This makes it a great choice for various culinary uses. There are many brands available around the world.

What’s wrong with dairy milk?
Many people are opting for oat after learning about the ethical, environmental, and health impacts of dairy.
Dairy milk is worse for the environment than plant-based alternatives. Compared to dairy and some other plant-based alternatives, oat milk typically has a lower environmental footprint. For example, dairy requires ten times more land than oat to produce the same amount of end product. It also requires significantly more water to produce than oat milk. Dairy also generates far more greenhouse gas emissions.
Moreover, many people consider dairy production to be unethical. It involves forcibly impregnating cows and removing their calves from them shortly after birth so their milk can be taken and sold, which is known to cause distress to both mothers and calves.
Oat milk also has a range of health benefits over dairy. Dairy milk has been linked to various health problems, including cancer, while a recent study found that swapping away from dairy could boost heart health. Commercially produced oat milk is often fortified with additional nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and B vitamins, though you should always check the label as ingredients vary.
Why is oat milk so popular?

For all the reasons above, more and more people are making the swap from dairy to oat.
The popularity of oat milk is also due in part to the fact that it’s accessible to many people. As oats are free from dairy, nuts, and soy, they are a great choice to improve access for people with allergies. Oat milk is usually gluten-free too.
Dairy, on the other hand, is widely inaccessible. Some 70 percent of the world’s population is lactose intolerant, with the figure rising to 75 percent for Black and Latinx people.
How is oat milk made?
Oat milk is easy to make. Before you decide to make your own, you may want to bear in mind that commercial products usually come fortified with vitamins and minerals. If you only drink homemade oat milk, you should think about where these vitamins are coming from in your diet.
Recipes for oat milk are easy to find online. Try this one from Simple Vegan Blog or another from Nora Cooks that takes just five minutes.
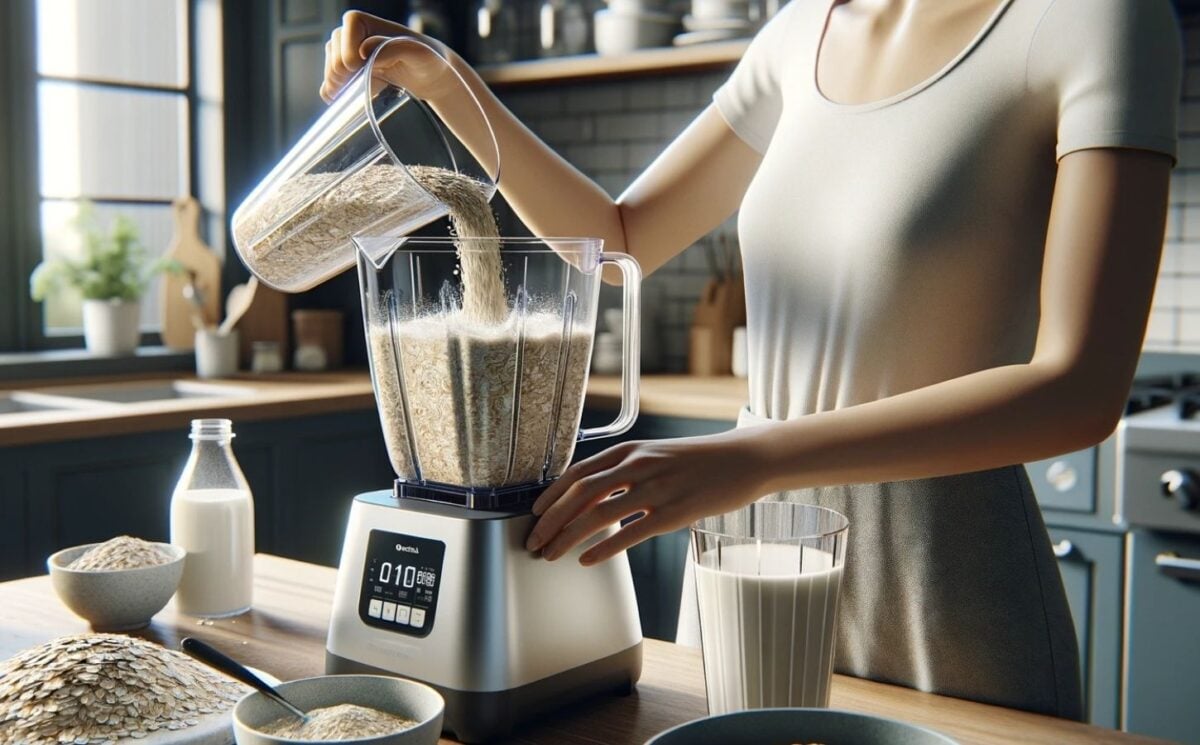
Getting the perfect glass of oaty goodness is actually a relatively simple process. It involves blending oats with water and then straining the mixture to separate the liquid from the solid components.
Generally, the oat milk production process looks as follows:
Soaking the oats
First, soak oats in water to soften them and make them easier to blend. The soaking time can vary, but it generally lasts about 30 minutes to an hour.
Blending
After soaking, blend the oats (and water) until the mixture is smooth. Optional: add additional water during blending to achieve the desired consistency.

Straining
Strain the blended mixture through a nut milk bag or a fine mesh strainer. This separates the liquid from the oats and other solid residues. This straining process may be repeated multiple times to ensure a smooth, creamy texture.
Flavoring and fortification
You have oat milk! The liquid can be left as is or it can be flavored and fortified. Common additions include salt, sweeteners (like sugar or dates), and flavors (like vanilla or cocoa). It can also be fortified with vitamins and minerals (like calcium, vitamin D, and B12) to enhance its nutritional profile.
Homogenization and stabilization (for commercial products)
In commercial operations, it may undergo homogenization (to ensure a uniform texture) and be treated with stabilizers or emulsifiers to prevent separation and extend shelf life.
Storage
Commercial products are usually pasteurized for longer shelf life and can be stored unrefrigerated until opened. Homemade stuff should be stored in the fridge.
What brands are available to buy?
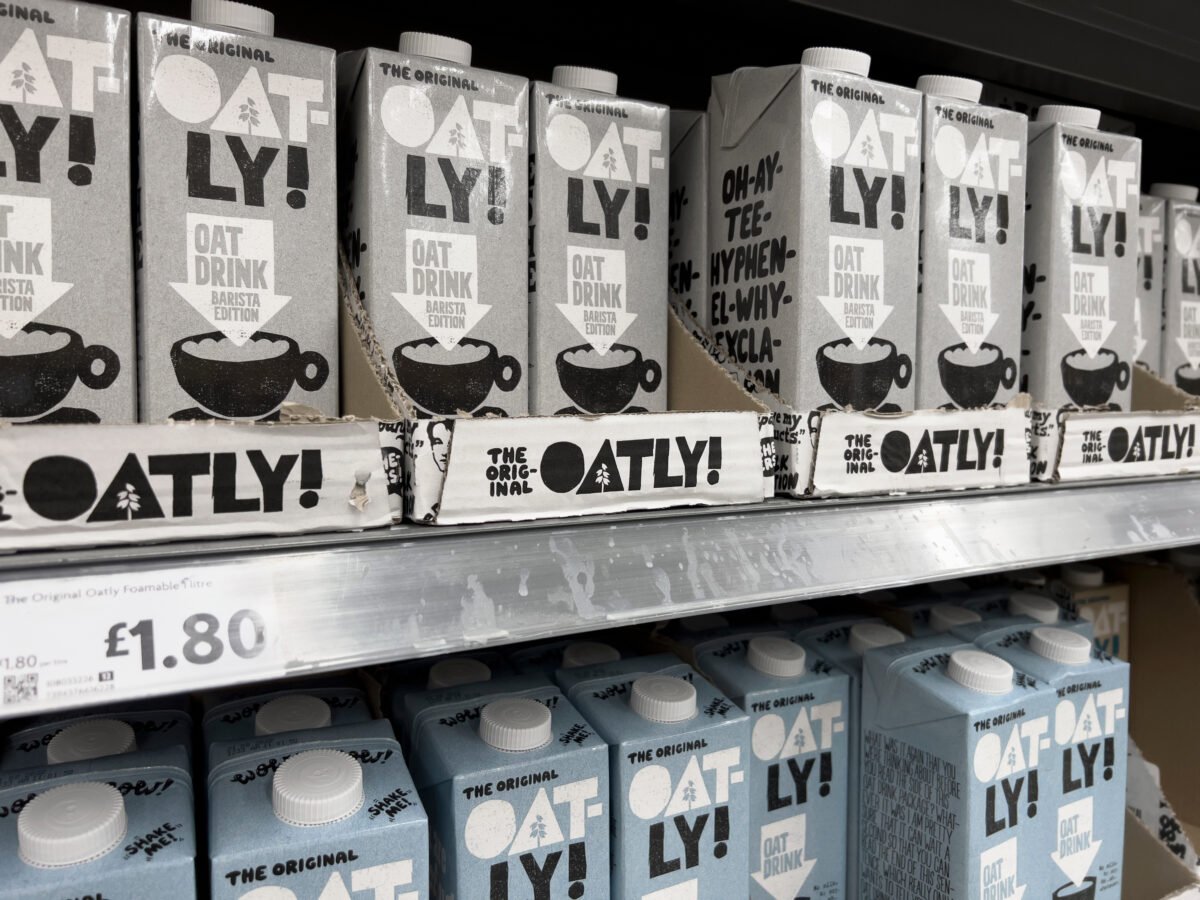

With the surge in the popularity of plant milks, it is now possible to buy the oaty stuff in many mainstream shops.
Big brands such as Oatly and Califia Farm are available internationally. Popular US brands include Planet Oat and Silk. UK favorites include Minor Figures and PureOaty. In Europe, Alpro leads the way.
More recently, a huge range of supermarkets have also released their own-brand labels, offering a cheaper option. The cost of dairy has soared in the past few years, making oat milk a good-value option for budget-conscious shoppers.